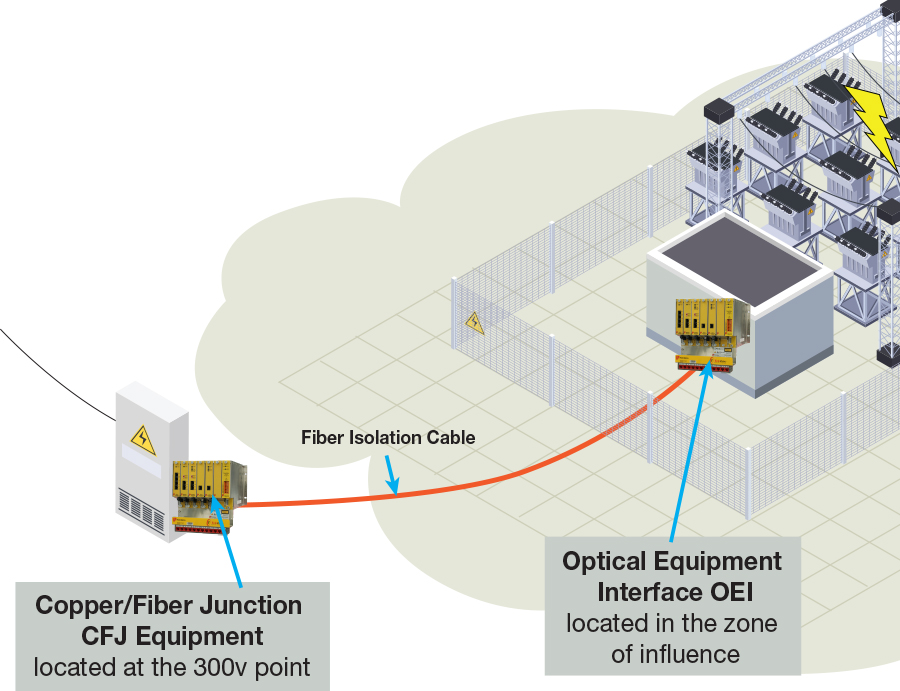
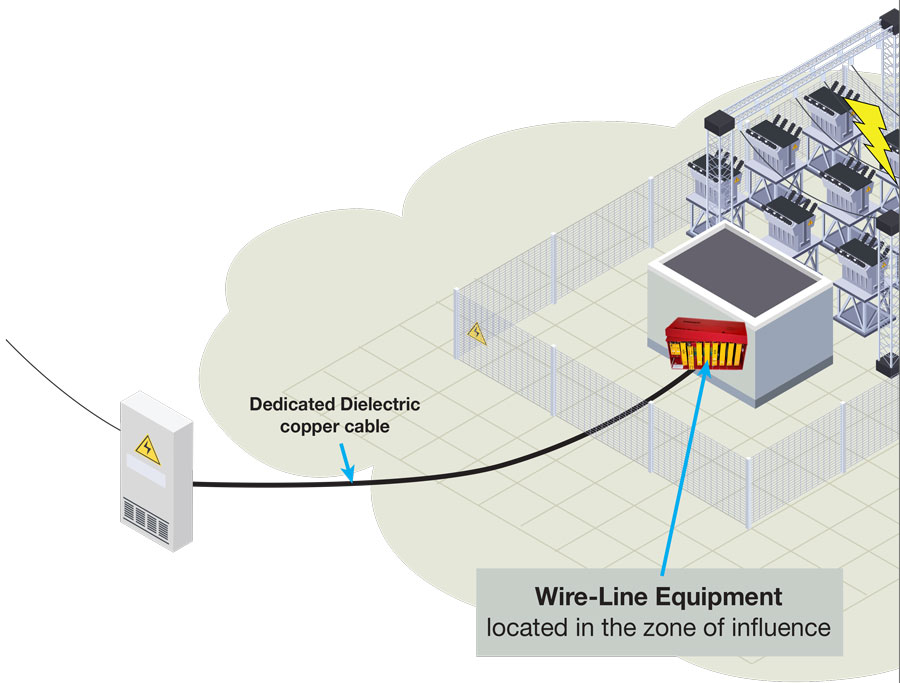
Why is High Voltage Isolation Important?
- To ensure personnel safety
- To protect telecom equipment from damage
- To provide reliable service to mission-critical circuits used for:
- Power system protective relaying (teleprotection)
- SCADA, transformer monitoring, Digital Fault Recording (DFR)
- Video surveillance & security (CIP requirements)
- Control Center telecom circuits
- Wireless site service
- To isolate telecom circuits from high voltage energy during:
- Power fault conditions
- Lightning discharge
- Electromagnetic Induction (under built lines)
Ground Potential Rise (GPR) Event
IEEE Standard 487 defines Ground Potential Rise (GPR) as: When a power system ground fault occurs, all or some of the fault current returns via the earth through the ground grid and produces a potential difference between the ground grid and remote earth. A potential difference between two ground planes connected via a conductor (like a wireline communications circuit) will produce a current. This ground fault current causes damage to equipment tied to the conductor.
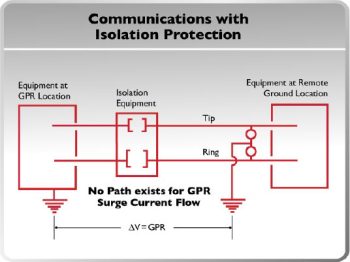
Communications with Isolation Protection
If the wireline is properly isolated, the same GPR will not cause any damage, since the two ground planes (Station and CO) are completely isolated from each other.
General Safety Considerations
- Hazardous voltages can appear suddenly as a result of power faults or lightning strikes (which produce transient Ground Potential Rise)
- Conductive objects can become energized or carry a harmful potential that, if not properly protected, can cause serious injury
- Personnel safety can be achieved through (1) education, (2) proper facility design and (3) use of approved/tested insulated safety equipment
- Rubber-soled shoes, rubber gloves and dielectric (insulated) mats can provide insulation to minimize touch and step potentials
- Definitions:
- Touch potential is the difference between the voltage gradient that one is standing on and the voltage gradient that one is touching; a significant difference in touch potential can be hazardous.
- Step potential is the difference in voltage gradients between a person’s two feet.
- GPR: “…the product of a ground electrode impedance, referenced to remote earth, and the current that flows through that electrode impedance.” The total station GPR is equal to the product of the station ground grid impedance and that portion of the total fault current that flows through it. [per IEEE Stds. 487 and 367]
Isolation of Critical Communications Circuits The 5 W’s
Who should be aware of the need to isolate?
- Facilities requiring service over a copper wireline going into a high voltage environment or where a GPR event can occur
What is isolation equipment?
- A device allowing telecommunication signals to pass through transparently, while blocking high voltage surges
Where should isolation be used?
- Power plants, substations, wireless facilities, wind farms, E9-1-1 sites
Why should you isolate wireline circuits in high voltage environments?
- Prevent personnel injury, equipment damage and loss of valuable data
When should isolation be used?
- Calculated GPR is over 1000V peak asymmetrical
- Class A service is required
- Risk of lightning strikes or high voltage surge at the site where communication services are required
- Where the service is provided over wireline